All Tags
AWS
ai
algorithm-design
architecture
browser
cloud
cloud-efficiency
cloud-principles
cost-reduction
data-centric
data-compression
data-processing
deployment
design
documentation
edge-computing
email-sharing
energy-efficiency
energy-footprint
enterprise-optimization
green-ai
hardware
libraries
llm
locality
machine-learning
maintainability
management
measured
microservices
migration
mobile
model-optimization
model-training
multi-objective
network-traffic
parameter-tuning
performance
queries
rebuilding
scaling
services
storage-optimization
strategies
tabs
template
testing
workloads
Tactic: Hardware multiplication
Tactic sort:
Dark Tactic
Type: Unsustainable Pattern
Category: edge-computing
Tags:
Title
Hardware multiplication
Description
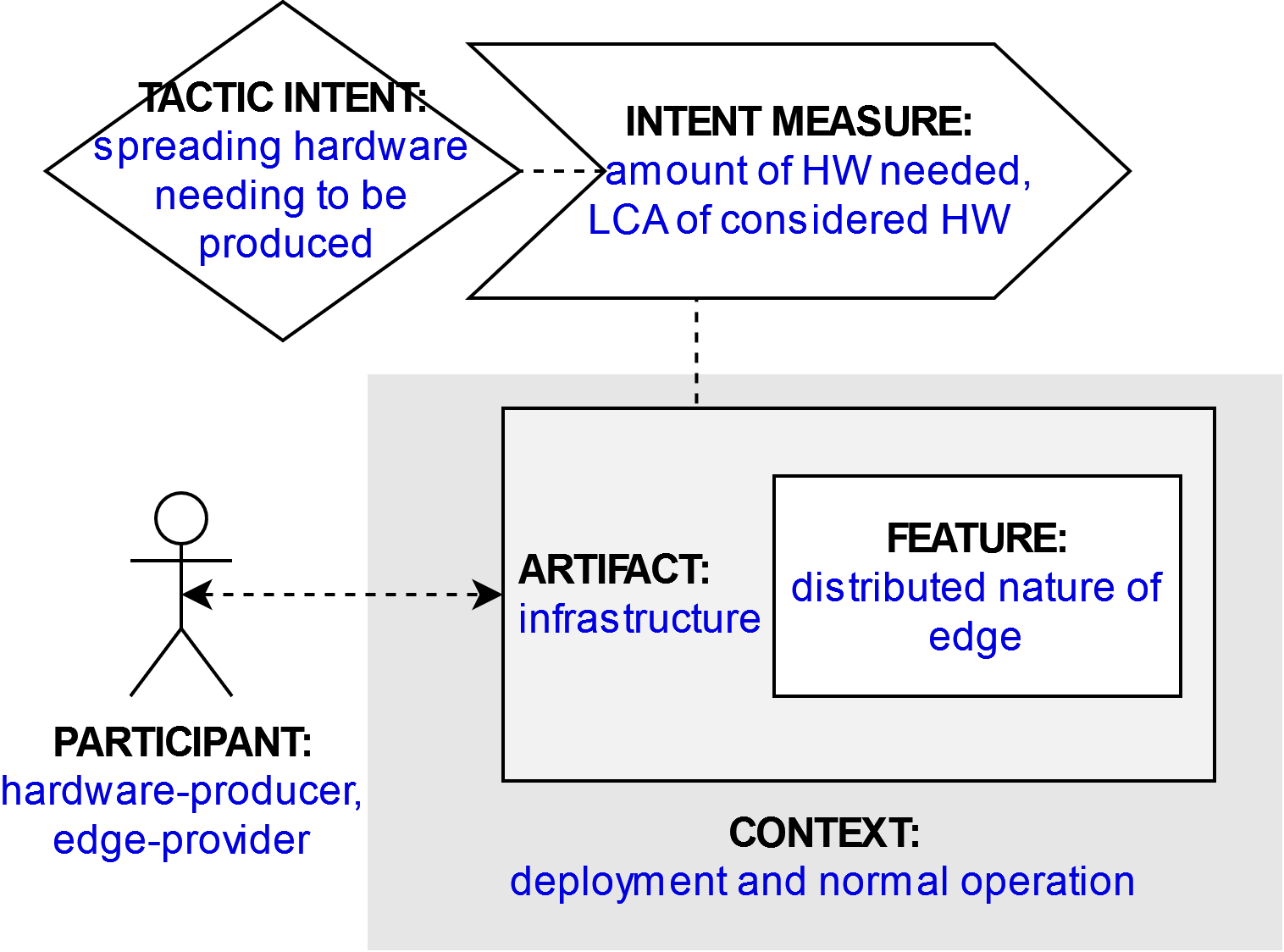
The distributed nature of edge computing leads to a lot of hardware being produced. This has an impact on resource utilization that has to be investigated both for producing them but also for running them, i.e. to perform lifecycle assessments. As part of this effort, Pirson & Bol provide a carbon footprint assessment of IoT edge devices (focusing on the production and transport phases) that shows the consequent impact these devices have.
Participant
hardware-producer, edge-provider
Related artifact
Infrastructure
Context
Deployment and normal operation
Feature
Distributed nature of edge
Tactic intent
Spreading hardware devices that need to be produced
Intent measure
Amount of hardware needed, Life cycle assessment of the hardware considered
Countermeasure
Use already existing devices as edge devices (for example embedded systems) instead of building dedicated edge devices.
Source
*The Dark Side of Cloud and Edge Computing* by Klervie Toczé, Maël Madon, Muriel Garcia and Patricia Lago (DOI: https://doi.org/10.21428/bf6fb269.9422c084)Graphical representation