All Tags
AWS
ai
algorithm-design
architecture
browser
cloud
cloud-efficiency
cloud-principles
cost-reduction
data-centric
data-compression
data-processing
deployment
design
documentation
edge-computing
email-sharing
energy-efficiency
energy-footprint
enterprise-optimization
green-ai
hardware
libraries
llm
locality
machine-learning
maintainability
management
measured
microservices
migration
mobile
model-optimization
model-training
multi-objective
network-traffic
parameter-tuning
performance
queries
rebuilding
scaling
services
storage-optimization
strategies
tabs
template
testing
workloads
Tactic: Trust overhead
Tactic sort:
Dark Tactic
Type: Unsustainable Pattern
Category: edge-computing
Tags:
Title
Trust overhead
Description
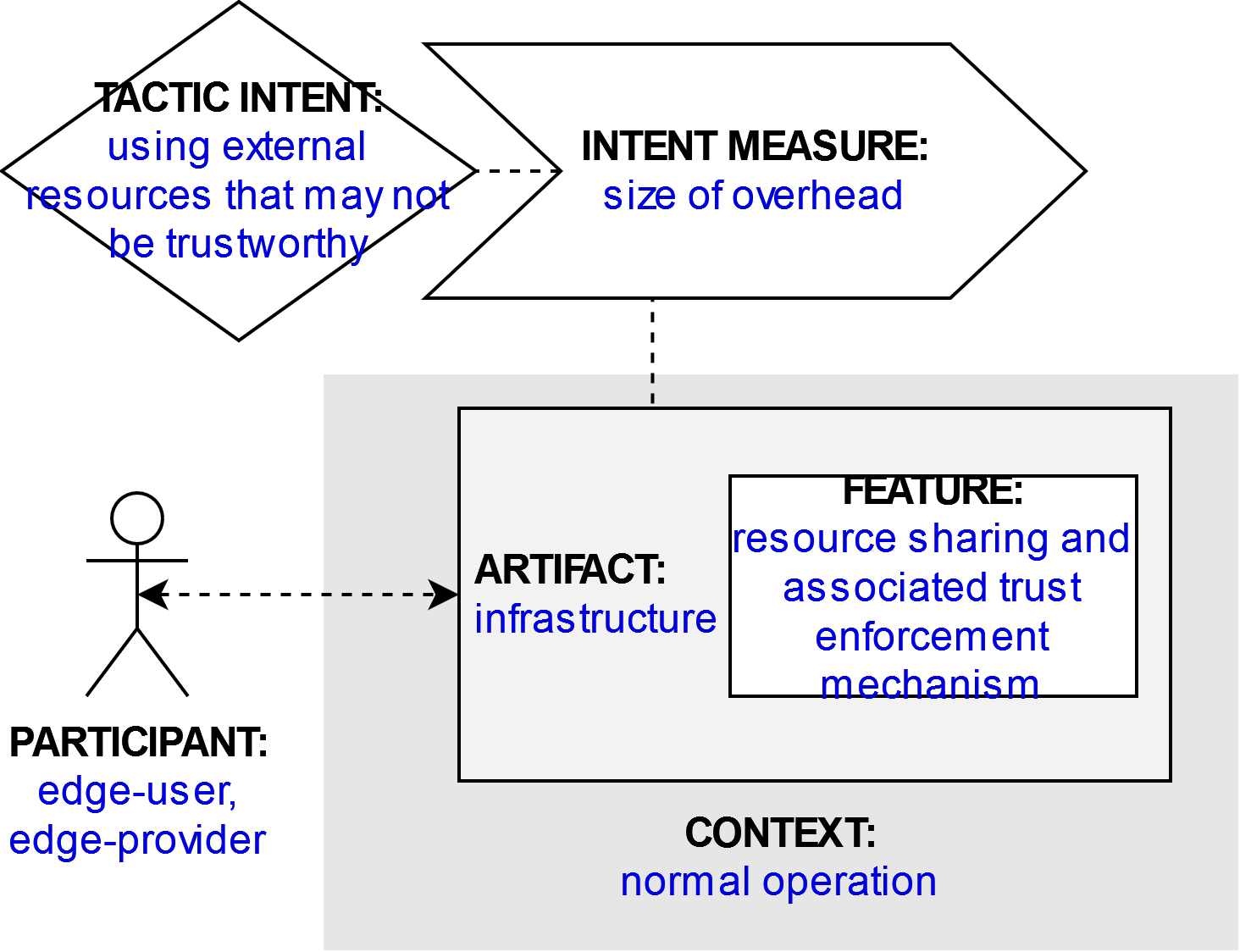
Edge computing creates new unforeseen security and privacy issues considered in the dark tactics security overhead, redundancy overhead and trust overhead. Literature on these topics comes up with edge-specific mechanisms to counteract them, as already touched upon in the dark tactics unauthorized surveillance and one-sided infrastructure control. However, these mechanisms almost always require extra com putation to be performed e.g., for encryption and decryption in case of security, or for establishing trust between devices. The overhead is also present in the network as additional metadata become needed in the payloads. At the same time, in order to offer uninterrupted provisioning of edge computing applications, redundant resources must be set up, which increases the environmental impact. Certainly, smarter mechanisms can still be developed to increase security, guarantee continuity of service or establish trust at lower cost. One could also ask if these overheads are significant enough to matter.
Participant
edge-user, edge-provider
Related artifact
Infrastructure
Context
Normal operation
Feature
Resource sharing and associated trust enforcement mechanism
Tactic intent
Using resources on an external devices that may not be trustworthy
Intent measure
Size of overhead
Countermeasure
A first step would be to generalize the evaluation of the extra environmental cost (or at least the extra computation and communication required) of any such mechanisms and compare it with the concurrent approaches.
Source
*The Dark Side of Cloud and Edge Computing* by Klervie Toczé, Maël Madon, Muriel Garcia and Patricia Lago (DOI: https://doi.org/10.21428/bf6fb269.9422c084)Graphical representation